Linear Data Simulation and Fit¶
This notebook creates linear data with noise and fits it. The residuals of the fit and their distribution is also displayed.
This code generates a line $f(x)= m\times x+b$, from X_MIN to X_MAX with a random number added from a gaussian distribution with zero mean.
Uses packages
Example output :
Output of interact_with_plot()
| Linear Plot With Small Noise and Negative Slope | Linear Plot With Large Noise and Positive Slope |
|---|---|
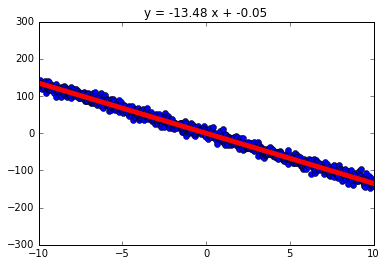
|
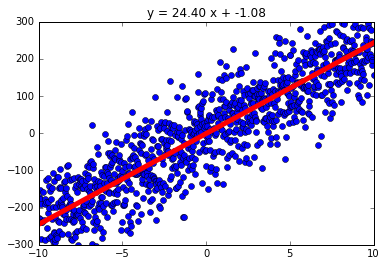
|
__Output of interact_with_residuals()__
| Linear Plot And Residuals With No Noise and Positive Slope | Linear Plot With Noise and Positive Slope |
|---|---|
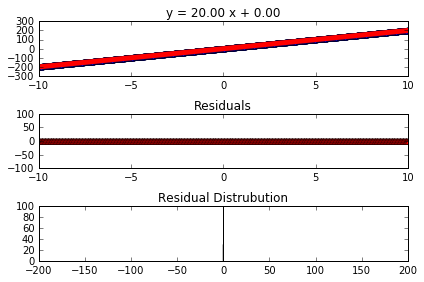
|
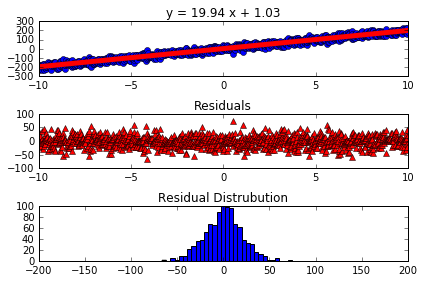
|
In [4]:
# import needed libraries
import numpy as np
import scipy.optimize as so
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ipywidgets import *
import random
from types import *
import math
# Define Constants
# Constants that determine the span of the line in the x-axis
X_MIN=-10
X_MAX=10
ListType=list
# Define Functions
# Define a function that finds the optimized least squared fit to a function
def fit(function,xdata,ydata,a0):
"Fit returns a least square fit "
error_function=lambda a, xdata, ydata:function(a,xdata)-ydata
a,success=so.leastsq(error_function, a0,args=(xdata,ydata))
return a
# Define a linear function
def line_function(a,x):
"line function (y=a[1]x+a[0])"
return a[1]*x+a[0]
# Define a function that finds residuals given a fit function and fit parameters and an original data set
def find_residuals(fit_function,fit_parameters,x_data,y_data):
"""Returns the residuals for a fit"""
if type(x_data) in [np.ndarray,ListType]:
output=map(lambda x:fit_function(fit_parameters,x),x_data)
if type(y_data) is not ListType:
raise
output=[f_x-y_data[index] for index,f_x in enumerate(output)]
elif type(x_data) is FloatType:
output=fit_function(fit_parameters,x_data)-y_data
else:
output=None
return output
# Define a function to plot a line and a fit through that line
def plot_line(noise_magnitude,number_points,slope,intercept):
"A function to plot a line with noise"
data_list=np.linspace(X_MIN,X_MAX,number_points)
y_data=[slope*x+intercept+random.gauss(0,noise_magnitude) for x in data_list]
results=fit(line_function,data_list,y_data,[1,0])
y_fit=[line_function(results,x) for x in data_list]
#plot the data
plt.plot(data_list,y_data,'ob')
#plot the fit
plt.plot(data_list,y_fit,'r-',linewidth=5)
ax=plt.gca()
ax.set_ylim(-300,300)
ax.set_title('y = {0:3.2f} x + {1:3.2f}'.format(results[1],results[0]))
plt.show()
# Define a plotting function that shows a line, a fit through that line, the residuals of the fit and a histogram
# of those residuals
def plot_residuals(noise_magnitude,number_points,slope,intercept):
"A function to plot a line with noise and the residuals of that fit including a histogram of those residuals"
data_list=np.linspace(X_MIN,X_MAX,number_points)
y_data=[slope*x+intercept+random.gauss(0,noise_magnitude) for x in data_list]
results=fit(line_function,data_list,y_data,[1,0])
y_fit=[line_function(results,x) for x in data_list]
#plot the data
# Comment this line to change the plot layout
fig, (ax0, ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=3)
# Uncomment these lines to change the laytout
# fig = plt.figure()
# ax0 = plt.subplot(221)
# ax1 = plt.subplot(223)
# ax2 = plt.subplot(122)
ax0.plot(data_list,y_data,'ob')
# plot the fit
ax0.plot(data_list,y_fit,'r-',linewidth=5)
ax0.set_ylim(-300,300)
ax0.set_title('y = {0:3.2f} x + {1:3.2f}'.format(results[1],results[0]))
# find the residuals
residuals=find_residuals(line_function,results,data_list,y_data)
# plot the residuals
ax1.plot(data_list,residuals,'r^')
ax1.set_ylim(-100,100)
# plot a histogram of the residuals
ax2.hist(residuals,bins=int(math.floor(math.sqrt(number_points))))
ax2.set_ylim(0,100)
ax2.set_xlim(-200,200)
# set the plot titles
ax1.set_title('Residuals')
ax2.set_title('Residual Distrubution')
# display
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# define scripts calling these create interactive plots
def interact_with_plot():
%matplotlib inline
interact(plot_line,noise_magnitude=(0,100,1),number_points=(10,1000,10),slope=(-30,30,.1),intercept=(-200,200,1))
# Test the find_residuals function
def residual_script():
data_list=np.linspace(X_MIN,X_MAX,1000)
y_data=[5*x+10+random.gauss(0,5) for x in data_list]
results=fit(line_function,data_list,y_data,[1,0])
print(find_residuals(line_function,results,data_list,y_data))
def interact_with_residuals():
%matplotlib inline
interact(plot_residuals,noise_magnitude=(0,100,1),
number_points=(10,1000,10),slope=(-30,30,.1),intercept=(-200,200,1))
In [5]:
#%matplotlib notebook
plot_residuals(10,1000,5,7)
In [6]:
interact_with_plot()
In [7]:
interact_with_residuals()